Built to preserve their value by being pegged to an external asset, stablecoins were first conceived byMastercoin founder J.R. Willettin 2012. Aware of the "instability" of bitcoin, Willet proposed that cryptos with a "stable value, pegged to an external currency or commodity" were needed.
Today there are three types of stablecoins. Ones collateralised by fiat such as cash or liquid short-term obligations. Ones that are backed by other cryptocurrencies and ones that maintain their peg via algorithms – with each type of stablecoin making the same promise of price stability.
Yet, the stablecoin industry is stable in name only. What was once virgin territory – first claimed by crypto's stalwarts of stability – has turned into a regulatory marshland. Now, unwanted adversaries equipped to traverse the terrain have set up camp. The fight for the future of money has begun.
Icarus
"The first scare for regulators was Libra. They [Libra] were directly trying to develop a competing monetary policy and this year you had Terra so it was clear regulators are now alert", Teana Baker-Taylor, head of policy EMEA atCircle, the firm behind stablecoin USDC, said.
Libra was a "bombshell", writes Henri Arslanian, the author of the Book of Crypto. Launched in 2019 by Meta, Libra set out to create a new global digital currency and infrastructure. Not only did Meta have 2.5 billion worldwide users at the time, it had the tech capabilities and funds to directly challenge monetary authority.
Overnight, the conversation of stablecoins and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) topped the agenda of regulators, who were just coming round to the unprecedented disruption blockchain and stablecoins could have on the financial system. Succumbing to regulatory pressure, Meta abandoned the project in January 2022.
However, a mere four months after algorithmic stablecoin terra (UST) depegged from its $1 parity to a low of 2¢. Terra and its sister company Luna lost $40bn and UST owners saw$18bn of their holdingsgo up in smoke. The subsequent contagion caused insolvencies of up to $600bn across the crypto space.
As Terra depegged so did other stablecoins. Market leader tether dropped to $0.956 and second and third largest stablecoins, USDC and BUSD respectively, traded at a premium of $1.01 – highlighting the innate fragility of the current stablecoin landscape.
Although Terra was the fourth largest stablecoin at the time, its collapse was not deemed systemic. However, the collapse of Tetherwhich accounts for45.6% of the market or USDC, $34.5, could very well be systemic.
Chart 1: Terra's downfall
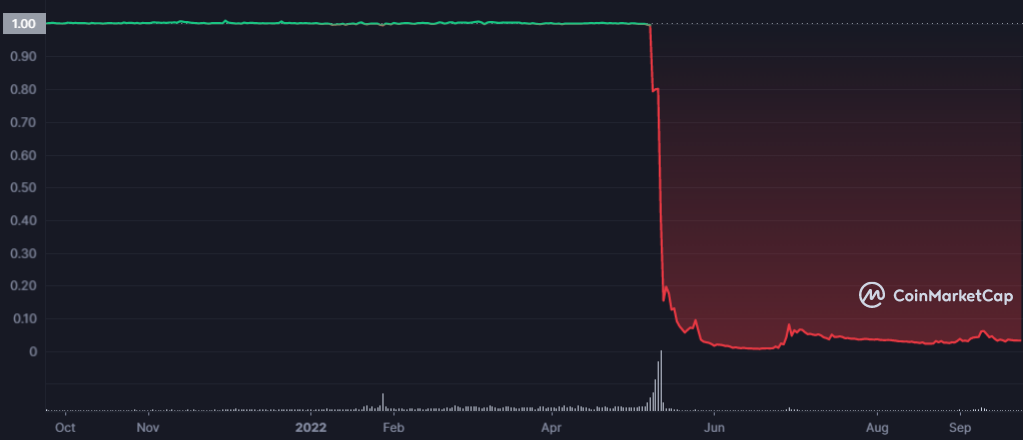
Source: CoinMarketCap
At the time of writing, stablecoins have a market cap of $153bn – a tenth of the entire crypto industry and almost three times larger than the US high-yield bond market.
Chart 2: Mayhem ensues
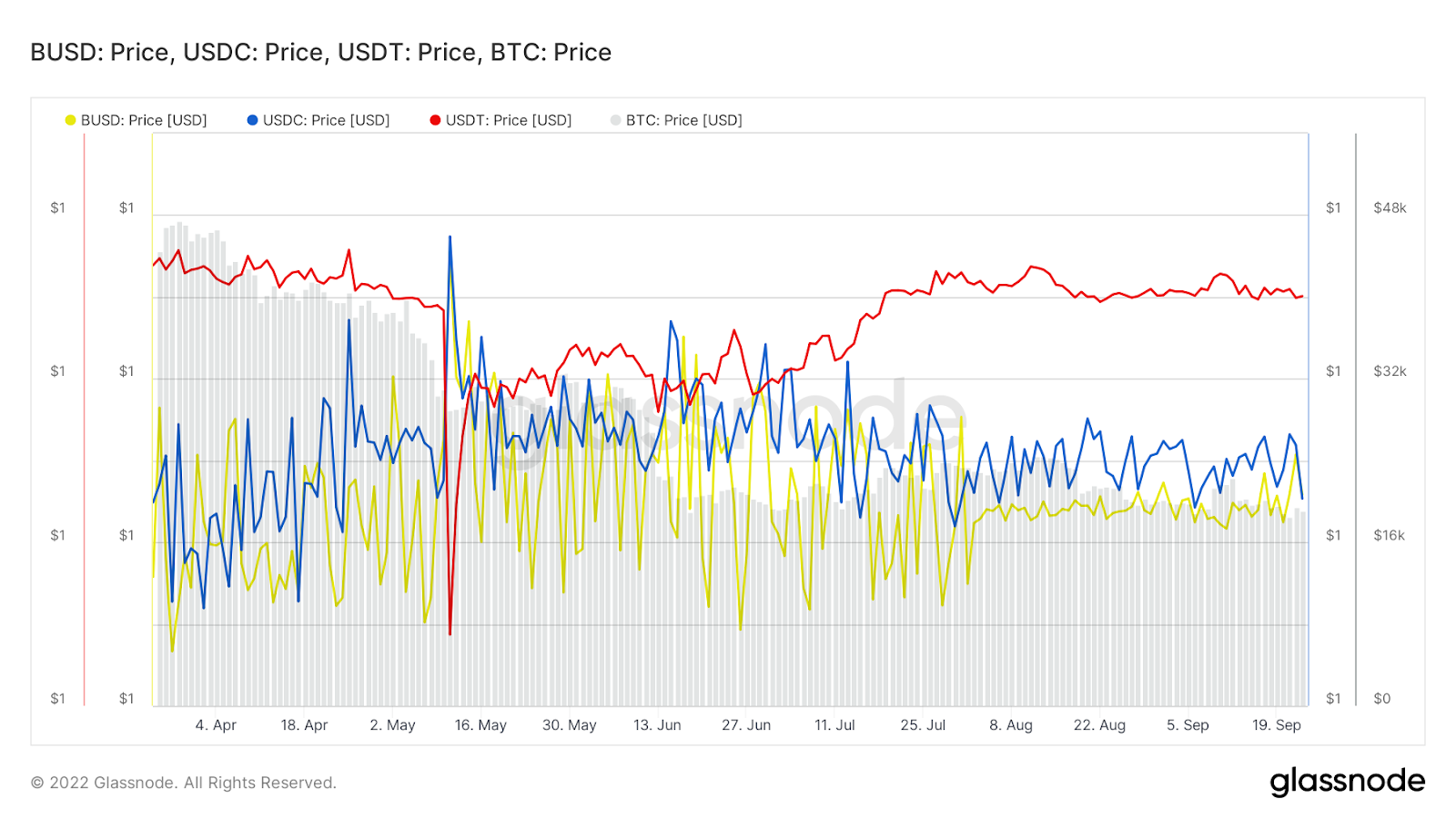
Source: Glassnode
Clamp down
"If stablecoins are going to become more widespread as a means of payment by retail consumers, protection will be key",Lisa CameronMP and chair of the digital asset all parliamentary group, told AltFi.
Jurisdictions across the globe have sprung to action following the Terra debacle. The UK unveiled itsFinancial Services and Markets Bill (FSMB) in July, defining stablecoins as "digital settlement assets", bringing them into the remit of regulators.
A month prior, the European Union agreed upon a provisional version of theMarkets in Crypto Assets (MiCa)framework, clarifying that stablecoin reserves must be "fully protected" against insolvency. MiCa also calls for a 1:1 backing – effectively outlawing algorithmic stablecoins.
Across the Atlantic, the Biden administration unveiled its first ever'Comprehensive Framework'for digital assets. Alongside President Joe Biden's recommendation, a bill proposed by Committee Chair Maxine Waters and Ranking Member Patrick McHenry is looking to seal a deal on stablecoin regulations.
According to Bloomberg, algorithmic stablecoins like Terra could bebanned for two years. Not only would algorithmic stablecoins be dealt with but traditional banks as well as non-banks could be given the right to issue stablecoins.
New arrivals
Just as regulators turn their screws on crypto-native stablecoin issuers, they are turning against themselves. Earlier in September Binance, the world's largest crypto exchange by volume traded decided tocut its competitorsfrom its platform.
USDC, Pax Dollar (USDP) and trueUSD(TUSD) will all be converted into BUSD, Binance's own stablecoin, at a 1:1 ratio by 29 September. BUSD is issued by Paxos who also run USDP, raising eyebrows at USDC issuerCircle.
A Circle spokesperson said that Binance's behaviour raised "potential market conduct questions."
Amid the in-sector bickering, private sector traditional initiatives have been emerging rapidly. In the UK, Digital FMI, Digital Pound Foundation and Millicent Labs are all preparing to challenge the current crypto-native stablecoin incumbents.
Digital FMI is a consortium coordinated by the Boston Consulting Group and IBM among others, while the Digital Pound Foundation is made up of members fromAccenture,CGI Group andRipple.
"Why should banks not have access to stablecoins, they will be the distribution mechanism for the digital economy," Brunello Rosa, the founder and head of research at Rosa & Roubini Associates, Digital FMI's economic advisor, said.
Digital FMI plans to launch a sterling-backed stablecoin inOctober and will prove a "private sector foothold" into the stablecoin market, Rosa added.
Central banks
While crypto-native stablecoin issuers are jumping hoops to meet regulator's demands, traditional finance is trying to break into the once crypto-native territory and central banks have been developing CBDCs.
CBDC's are a digital extension of central bank money and like stablecoins can track or be pegged to a countries fiat currency. Unlike stablecoins, CBDCs do not need to maintain a reserve of fiat collateral to equal the stable coins in circulation. Instead, CBDCs are backed by a countries central back and so are themselves a legal tender.
Additionally, CBDCs are considered a national bank solution, providing money transfer solutions between national banks, stablecoins instead have a retail focus.
According to CBDC tracker,105 countries acrossthe globe have started their own CBDC research projects – with 66 countries are actively researching CBDCs.
Although central banks are actively pursuing a CBDC, the gig may not be up for both crypto-native and traditional finance issuers – in fact, they may end up working hand-in-hand.
Chart 3: Digital money is the future
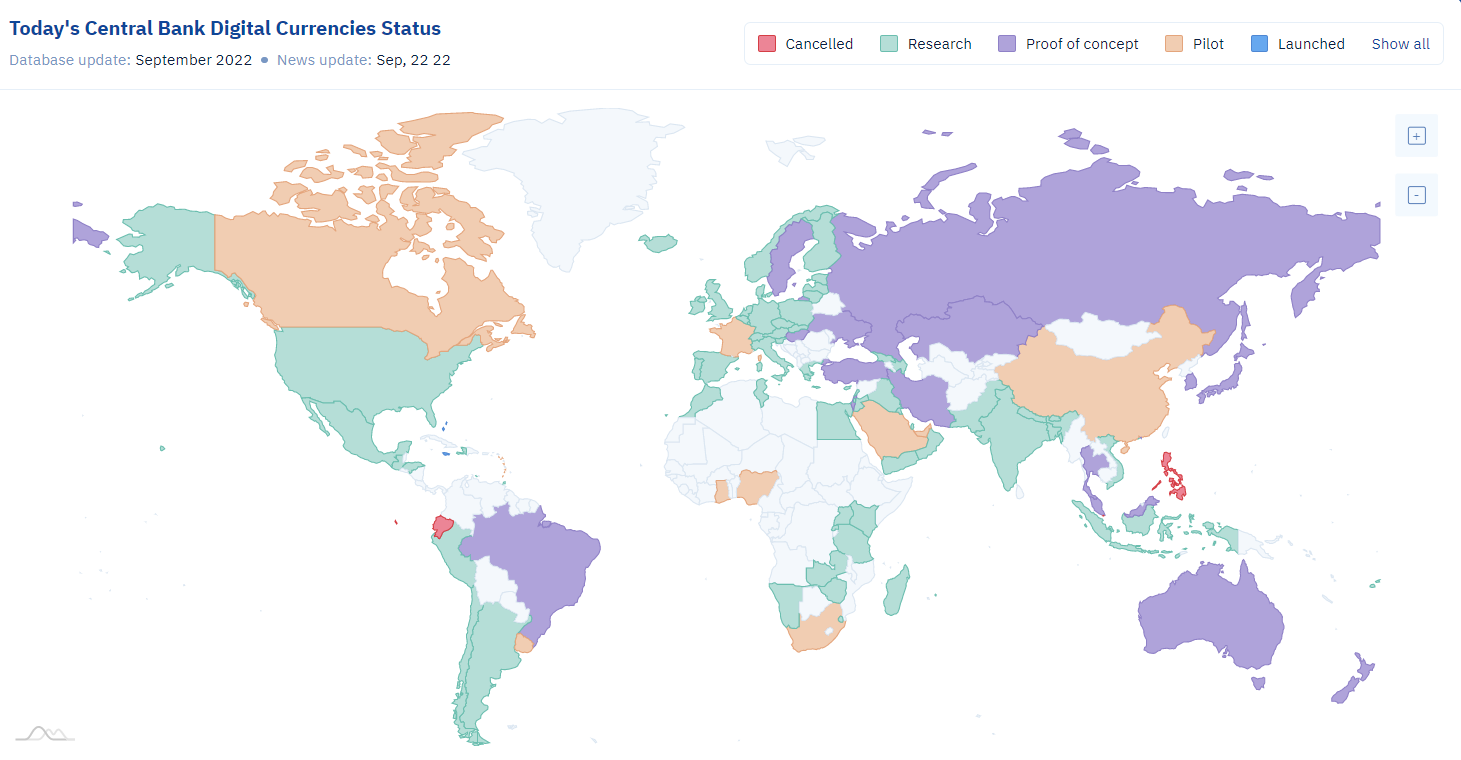
Source: CBDC Tracker
"Most banks, if one assumes that they will be the regulatory approved path, will need crypto native organizations to build them. Similarly, fintechs and non-banks that want to use stablecoins will need the crypto native issuers to build them", Sultan Meghji, professor at Duke University and former head of innovation at the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, said.
Both Baker-Taylor and Rosa are adamant that building the right infrastructure will be the key to their longevity. For crypto-native stablecoin issuers the building blocks and infrastructure are already there. However, regulatory scrutiny will provide their greatest obstacle.
Conversely, consortiums composed of denizens of traditional finance may have a regulatory advantage but will have to build a stablecoin infrastructure that can compete with the existing crypto-native solutions.
"We are at a point where they [stablecoins and CBDCs] are significant and regulators will have to carefully define what role they will play", Lavan Thasarathakumar, government and regulatory affairs director EMEA at GDF, said.
The race for the future of money is well and truly underway.
This story was originally published on AltFi as the first part of a three-article series on stablecoins.
Related articles:




